Optimizing Jewelry Casting for Mass Production: Techniques, Trends, and More
Jewelry casting for mass production is a meticulous process using master patterns to create molds fr…….

Jewelry casting for mass production is a meticulous process using master patterns to create molds from materials like silicone or metal, into which molten metal is poured to form detailed pieces. Techniques include lost-wax casting, investment casting, and centrifugal casting, employing precious metals and advanced methods to ensure consistent quality at lower costs. While accessible to wider markets, initial setup costs can be high, impacting competition; customization may also be limited compared to handcrafted jewelry. Best practices leverage advanced materials and technologies for enhanced efficiency, rapid prototyping, and sustainable practices, with 3D printing emerging as a trend.
Delve into the fascinating world of jewelry casting for mass production, a process that transforms intricate designs into accessible, affordable pieces. From understanding the fundamentals of casting techniques to exploring the materials and benefits, this article guides you through the entire spectrum. Discover how modern innovations are reshaping the industry while addressing key challenges. Uncover best practices and future trends, as we delve into the art and science behind jewelry casting, ensuring a vibrant and evolving market.
- Understanding Jewelry Casting for Mass Production
- Materials and Techniques Used in Jewelry Casting
- Benefits and Challenges of Mass-Produced Jewelry Casting
- Best Practices and Future Trends in Jewelry Casting
Understanding Jewelry Casting for Mass Production

Understanding Jewelry Casting for Mass Production
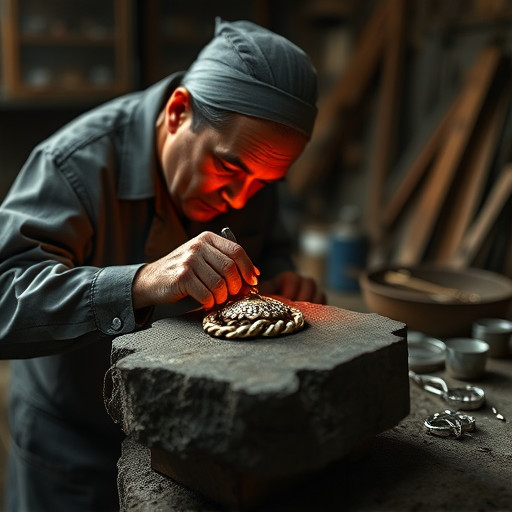
Jewelry casting is a manufacturing process that involves creating intricate designs in metal by pouring molten material into molds. For mass production, this technique becomes invaluable, enabling consistent reproduction of complex jewelry pieces at scale. The process begins with creating or acquiring a master pattern, which serves as the blueprint for the final product. This pattern is then used to form a mold, typically made from materials like silicone, rubber, or metal.
The molds are designed to capture every detail of the jewelry design, ensuring accuracy and precision in each cast. Molten metal, usually silver, gold, or base metals, is carefully poured into these molds under controlled conditions. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the piece is removed from the mold, undergoing various post-processing steps such as polishing, cleaning, and quality inspection to achieve the desired finish. This method allows for high production rates while maintaining the level of detail and quality that jewelry requires.
Materials and Techniques Used in Jewelry Casting

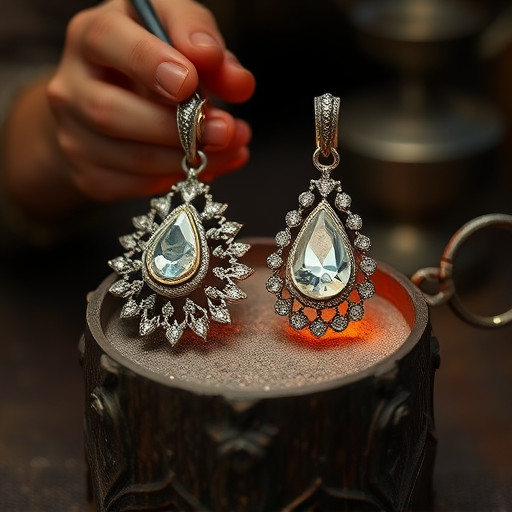
In jewelry casting for mass production, a variety of materials and techniques are employed to achieve high-quality, consistent results. Common choices for castable materials include precious metals like silver, gold, and platinum, as well as their alloys. These metals are selected based on their malleability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. The process often begins with preparing a master pattern, which can be made from various materials such as wax, resin, or even 3D-printed plastics.
The casting techniques used range from traditional methods like lost-wax casting, where a detailed wax model is created, encapsulated in a ceramic mold, and then melted out, leaving an empty space for the metal to fill. Modern approaches include investment casting, which involves coating the pattern with a refractory material to create a hollow form, and centrifugal casting, utilizing spinning molds to produce complex shapes efficiently. These methods ensure precision and allow for intricate designs in mass-produced jewelry pieces.
Benefits and Challenges of Mass-Produced Jewelry Casting

Mass-produced jewelry casting offers a range of benefits, revolutionizing the way jewelry is created and distributed. One of the primary advantages is the ability to produce complex designs at a lower cost per unit, making it accessible for brands to offer intricate pieces to a wider market. This process ensures consistency in quality and design, as each piece is cast from a single mold, eliminating variations often seen in handmade jewelry. Additionally, casting allows for rapid production times, enabling businesses to meet high demand quickly.
However, challenges exist within this efficient system. The initial setup cost for creating molds can be substantial, especially for smaller brands or independent designers. This barrier to entry may limit the ability of new businesses to compete in the market. Furthermore, mass production often prioritizes speed over customization, which can result in a lack of uniqueness and personalization that handcrafted jewelry is renowned for.
Best Practices and Future Trends in Jewelry Casting

Best practices in jewelry casting involve several key strategies for ensuring quality and efficiency in mass production. First, utilizing advanced materials like investment castings made from wax or polymer patterns offers unparalleled precision, allowing for intricate designs that were once challenging to produce. This method also facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling designers to quickly iterate and refine their work.
Future trends in jewelry casting are driven by technological advancements, with 3D printing emerging as a prominent game-changer. This technology allows for even more customization, complex geometries, and the potential to reduce waste significantly. Additionally, sustainable practices are gaining traction, with eco-friendly materials and processes being adopted to create jewelry while minimizing environmental impact. These developments promise to revolutionize the industry, making jewelry casting more accessible, efficient, and environmentally responsible.